Emerging markets continue to carry the brunt of the global shift towards renewable energy. The increased energy demand, coupled with dwindling fossil fuel supplies, low exports and the need to cut emissions, leads many developing economies to seek clean alternatives. Between these, solar and wind energy have emerged as the most favored options. Each represents enormous potential, the gap in usage between each, and the reasons therein, vary by their geography, policy frameworks, levels of investment, and infrastructure preparedness.
This paper studies the gap in solar and wind energy usage in developing economies and the gaps, opportunities and trends that are influencing the future of renewable energy in these parts.
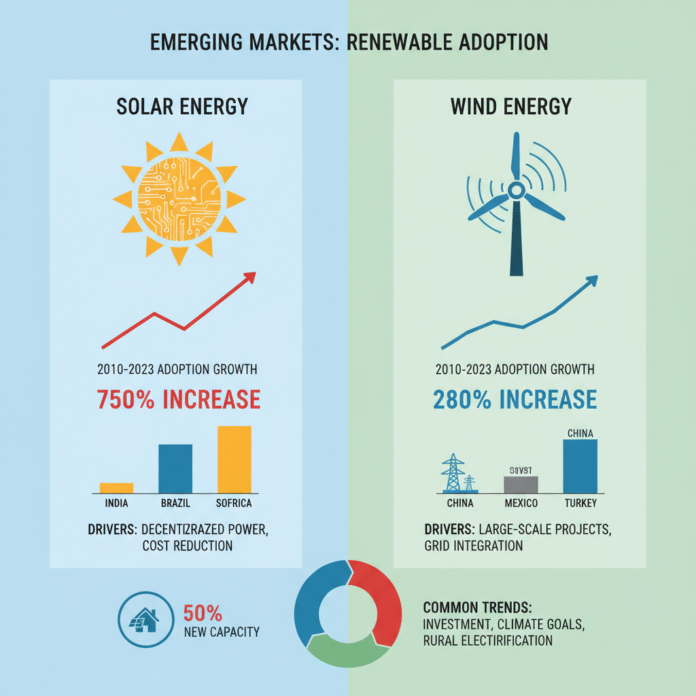
The gap in the usage of solar and wind energy in developing economies is steep. Emerging markets are projected to carry the most demand in the foreseeable future. The International Energy Agency (IEA) anticipates that 70 percent of all growth in global energy demand will come from developing markets situated in Asia, Africa, and Latin America. It is essential that these countries adopt renewable sources of energy to curb the dependence on fossil fuels.
Solar energy is most prevalent in countries with low solar irradiance, such as India, Brazil, and Kenya.
Wind energy can be harnessed at reasonably low cost in countries with low altitudes and relatively more coastal regions and consistent winds such as Vietnam, South Africa, and Mexican coasts.
Both types of technology afford the opportunity towards electrification, reducing foreign dependency, and foreign investment in the country.
Emerging countries and the prospect towards solar energy utilization
Benefits of solar energy
Abundant resource – Most of emerging countries are situated at the equatorial regions which receive sunlight for the better part of the year.
Scalability – Solar energy can be utilized in large or utility scale projects as well as in smaller off grid devices.
Lower Entry Barriers – The cost of installation of solar panels has relatively gone down making them more economically accessible to the households and the business sectors.
Remote Energy Access – Off grid solar systems can be deployed to provide cost effective energy in rural areas without electricity where electricity grid extension is economically unfeasible.
Obstacles to the adoption of solar energy
Insufficient battery storage for solar energy makes its use impossible for night time or in the absence of direct sunlight.
Collectively solar systems can be economically advantageous to rural communities as well as to the low income regions with the associated financing remaining a barrier to the adoption of renewable energy in many of them.
Public policy coordination is poor and lack of investment is a major barrier to the modern energy access.
Application of theoretical knowledge or case studies ought to be utilized to comprehend the processes better.
As of now, India stands as one of the foremost countries with best solar installation systems along with a targeted goal of 280 Gigawatts of solar capacity by 2030.
Moreover, Kenya is leading with decentralized solar to rural located households with the M-KOPA company which has pioneered the pay-as-you-go solar system in the country.
Adoption of Wind Energy in Emerging Markets.
Benefits of Wind Power.
High Efficiency. Wind turbines can generate a large amount of electricity in regions where winds are strong and steady.
Cost Competitive. In many emerging economies, wind has become one of the most inexpensive sources of new power generation.
Utility Scale Potential. Large wind farms are capable of providing substantial amounts of energy to national grids.
Obstacles to Wind Energy Usage.
Geographic Dependence. Wind projects are only feasible in certain locations where wind flow is consistent.
Land Use Problems. Large turbines require a considerable amount of space and this can create competition with farming and the local population.
Grid Interface. In many emerging economies, the grid infrastructure is insufficient to accommodate the more sophisticated wind generation.
Case Examples.
Brazil has invested significantly in wind energy and is now one of the largest wind markets outside of Europe and the US.
South Africa is constructing large-scale wind projects as part of the Renewable Energy Independent Power Producer Programme (REIPPP).
Factors for Adoption: Wind vs. Solar Energy
| Factors | Wind Energy | Solar Energy |
|---|---|---|
| Resource Availability | Geographically limited: offshore and mountain regions | Geographically unlimited: sun richer regions |
| Cost trend | Unaffordable for small sites | Rapidly decreasing, affordable |
| Scalability | Rigidly off grid | Flexible due to off grid |
| Infrastructure | Advanced grid & land required | None required off grid |
| Adoption | Impeded by region | Rapid, especially in urban areas |
Trends in Investment for Renewable Energy
With demand for renewable energy on the rise, many international investors have set their eyes on emerging economies as attractive destinations for investment. Organizations such as the International Finance Corporation and the World Bank offer financing, while private investors tend to focus on growing energy demand.
Due to decreasing risks and quicker deployment, solar energy investments are more prominent.
Wind investments concentrate on the countries where wind corridors are established and there is a favorable regulatory environment.
Investors have noted a higher concentration of interest in China, India, Brazil, and Vietnam as prime destinations for renewable investments.
Private Regulation and Policy Influence
Company regulations have the greatest impact on the integration of the renewables:
Special subsidies and credits: Solar and wind integration offer incentives to tax and finance.
Grid Expansion: Infrastructure is needed to support the intermittent solar and wind integration.
Public donations: Accelerates investment from private ventures to finance freely.
Analyzing the regulatory environment demonstrates that countries with consistent, reliable, and transparent policies are able to adopt renewables more quickly compared to countries with imbalanced regulations.
Emerging Market Opportunities
Hybrid Systems: Integrating solar and wind with battery storage to provide more dependable supply.
Green Hydrogen: Generating hydrogen for industrial use from surplus solar and wind energy.
Job Creation: Employment opportunities in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance are brought by renewable industries.
Decentralized Power: Mini-grids and off-grid systems help to increase electricity access in unserved areas.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Which is better for emerging markets: solar or wind?
It depends on the country’s geological and infrastructural capital. Solar is more geographically versatile and easier to deploy and wind is better for large scale generation if the country has favorable wind conditions.
- What are the main barriers to renewable adoption in emerging markets?
Emerging markets face the challenge of high initial expenditures, unstable policies, poor grid infrastructure, and access to financing.
- Why is solar more common in rural electrification projects?
Prototypes of solar panels are the most affordable, most convenient to install, and most able to furnish energy to small communities or households that are not geographically positioned to benefit from a grid.
- Which countries are leading renewable adoption in emerging markets?
Countries that are considered the leading in deploying renewable energy are India, Brazil, Vietnam, Kenya, and South Africa.
- What are the perceptions of investors on renewable projects in emerging markets?
Investors are bullish because of the increasing demand for energy, but seek demand policies coupled with infrastructure reliability.
Forecast on Solar and Wind in Emerging Markets
Adoption of solar and wind energy in emerging markets is expected to pick up in the coming decade. Solar and wind technology costs are decreasing, resulting in international financing and supportive governmental policies allowing renewable energy to take a leading role in sustainable development.
Solar energy is expected to dominate rural electrification and small-scale solutions.
Wind energy will continue expanding in areas with strong infrastructure, especially along the coasts and in high-wind regions.
The most resilient and cost-effective approaches are likely to come from hybrid solutions integrating both technologies.